Your immune system plays a critical role in living a long and healthy life.
What Does Immunity Mean?
Immunity is how well you can fight off a particular virus, infection, or disease.
There are two types of immunity: 1) Innate and 2) Acquired.
Innate immunity is what you are born with, while acquired immunity is developed during your life as you are exposed to new environments and experiences.
What is the Immune System?
Your immune system is your body’s defense against infection and disease.[1] It is made up of 5 main components:
- white blood cells
- antibodies
- the complement system
- the lymphatic system
- bone marrow
What Causes a Weak Immune System?
There are many different factors that affect a weakened immune system. Genetics and epigenetics play a role as many people are born with immunocompromising conditions.
Your age is another factor in immunity. As you age, your immune system is weakened. This is because less B and T cells are being produced. The functioning of mature lymphocytes also decreases.[2]
Nutrient deficiencies play a role in immune system regulation, too. While the research in this area is not extensive, we know that particular vitamin and mineral deficiencies can result in weakened immunity.
For example, vitamin A deficiencies are associated with compromised immunity, as well as deficiencies in vitamin C and vitamin D (source)[3] [4]
In addition, the foods we eat affect our immune systems. A typical Western diet is high in inflammatory foods, such as processed and packaged meals, fast food, trans and saturated fats, and sugar.
Here’s why you want to avoid the following foods in excess to support a healthy, strong immune system:
#1. Sugary sweets like baked goods, candy, etc.
Research in the 70s discovered that after you consume sugar, your immune response is lowered for a couple of hours.[5]
You can imagine what this would mean if you consume sugar at breakfast, lunch, dinner, and between meals. Newer research found that while this may not be the case for viral infections, it remains particularly true for bacterial infections.[6]
#2. Alcoholic beverages
Alcohol disrupts several of the pathways involved in the immune system response. Drinking alcohol negatively impacts the microbes of your gut microbiome.[7]
It also damages epithelial cells, T cells, and neutrophils which are all critical for immunity. Once the gut microbiota is altered, the liver’s immune system is activated and an inflammatory response occurs.
Both chronic drinking, and acute binge drinking, have negative consequences on your immune system. For more information on the effects of alcohol, see this article on red wine consumption.
#3. Fried foods
Many fried foods, like French fries and donuts, contain acrylamide which is produced in the process of frying carbohydrates. Acrylamide is a carcinogen that has been associated with the development of autoimmune disorders and cancers.[8]
#4. Processed and packaged foods
A typical Western diet is filled with processed and packaged foods. Studies show that the high intakes of sugar, salt, and fat that are often found in these foods negatively impact your immune system.[9]
#5. Refined oils
Consuming refined oils can increase free radicals in your body. These increase oxidative stress and damage cell membranes, DNA, and lipids. If you’re going to use oil, choose a cold-pressed oil like avocado or extra virgin olive oil which are still intact with their fatty acids and vitamin E properties.
#6. Red meat
In 2015 the WHO classified red meat as a probable carcinogen.[10]
A sugar found in red meat, pork, and lamb, known as N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NeuG5c), has been found to increase systemic inflammation. Over a long period of time this can result in higher levels of cancers.[11]
#7. Dairy
Cows’ milk has several components that can harm our immune system.
Beta casein has been shown to increase an immune response, inflammation and have negative gastrointestinal effects.[12]
The NeuG5c sugar found in meats is also found in milk products.
Switching to non-dairy milk, like oat or almond milk, is an easy alternative that is not only better for your health but also more sustainable for the planet.
#8. Caffeine
Caffeine is dehydrating and hydration is important for immunity. Too much caffeine can also increase cortisol, the stress hormone, which can compromise our immunity.
However, some studies have found that low to moderate consumption may have a beneficial impact on immunity.
What are the Signs of a Weak Immune System?
If you get cold or flu often, this is a sign of a weakened immune system. In addition, feeling fatigued or lethargic often is another indicator.
How to Improve Your Immune System?
Our daily habits can improve our immune system. This includes everything from our diets, exercise routines, sleep habits, stress management, and mindset.
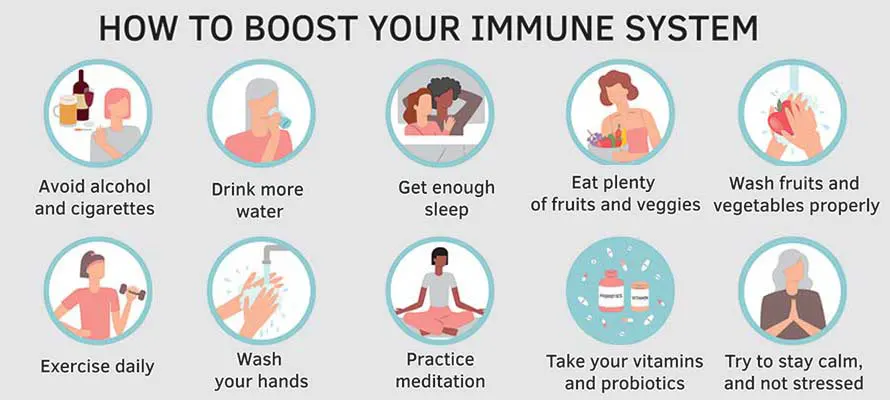
Ways to boost the Immune System. (Image Credit: Shutterstock)
Food to Build Your Immune System
A whole-food, plant-based diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains is a good starting point for boosting immunity through our food.
Best Vitamins for the Immune System
There are a number of vitamins and minerals that support immunity including Zinc, vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin A, vitamin B6, iron, selenium, beta-carotene, and magnesium.
Check out this article for more information on these nutrients.
Immune System Supplements
Supplementing with herbs, such as green tea, turmeric and medicinal mushrooms, may be effective for increasing immune functioning.
Immune Support is a herbal supplement that contains these three herbs as well as vitamins C and E.
EXPLORE – Best Immune Booster Supplements In 2025 | Tried and Tested
Hydrate, Hydrate, Hydrate
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day supports a healthy immune system. Adequate water consumption ensures that blood and lymph are flowing throughout your body.
These biological processes are essential for nutrients to get to the organs, and for waste to be removed.
Does Exercise Increase or Decrease Immunity?
Regular exercise which is light to moderate in intensity can strengthen the immune system.
You want to avoid strenuous exercise as this can weaken our immune system. Intense physical activity can place stress on our body, which affects immunity.
Stress Management
You’ve probably heard stress matters. But how important is stress for immunity?
The importance of managing stress can not be emphasized enough. When we are in a state of stress, our levels of cortisol rise which leads to handfuls of other negative outcomes.
High cortisol can look like a number of symptoms such as:
- Unexplained weight gain
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Acne
- High blood pressure
- Lack of sleep
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
- Depression
There are many ways to manage stress. Both yoga and meditation and wonderful tools for managing stress. Studies have found that people who regularly practice mindfulness meditation get sick less often.[13]
The Power of Positive Thinking
Dr. Frederick Lenz, an author, and teacher, once said “The most powerful force to maintaining a good immune system is the power of positive thinking and not allowing yourself to be unnecessarily drained emotionally by worries and fears.”
Our minds are powerful. Studies show that how we think affects how we feel, both positively and negatively. Optimistic people may live longer and have better longevity.[14]
Research has demonstrated that when stressors are brief (lasting less than a week), women who are optimistic had increased immune functioning compared to women who are pessimistic.[15]
However, when stressors last for longer periods of time, optimism may decrease immune functioning. The reasons for this discrepancy are unknown.
ALSO READ – A Beginners Guide to Holistic Health & Why It’s Important
The Importance of Boundary Setting
Whether optimism affects immunity seems to depend on the circumstance and our choice whether to engage or disengage with the stressor.
Sometimes optimism can lead to greater engagement with the stressor, which then increases cortisol levels. Increased cortisol lowers immunity.
This is where the boundary setting may come into play. If we set boundaries around the information we are taking in, and the people we are surrounding ourselves with, we can allow ourselves to disengage from the stressor, and perhaps still maintain optimism.
Another Reason to Quit Smoking
Smoking cigarettes weakens your immune system. Earlier we discussed acrylamides. Smokers have the highest blood levels of acrylamides.[16]
Don’t Forget About Sleep
One of the best actions we can take to boost immunity is to get a good night’s rest. For many insomniacs and night owls, this can be challenging. Try and aim for 7-9 hours of sleep a night.[17]
Sleep hygiene is one way to help support better sleep. This means turning off electronics two hours before bed, avoiding caffeine in the afternoon and evening, setting a consistent bedtime and wake time, and sleeping in a dark room.
Exposure to daylight upon waking will help sleep-wake cycles, as well.
Various sleep supplements may help you get a better night’s rest, too. Magnesium and zinc help modulate the nervous system, while melatonin can be helpful for a sleep reset.[18] [19]
SEE ALSO – The Best Over The Counter Sleep Aids and Natural Sleeping Pills
Conclusion
To conclude, our immune systems are complex. There are multiple factors, some of which are out of our control, but many which we can control through lifestyle changes.
It can be overwhelming to try to make a bunch of changes at once, so we suggest choosing a few lifestyle changes at a time, and adding more in overtime.
19 SOURCES
Health Insiders uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial policy to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
[1] Immune system explained - Better Health Channel https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/immune-system
[2] Montecino-Rodriguez E, Berent-Maoz B, Dorshkind K. Causes, consequences, and reversal of immune system aging. J Clin Invest. 2013 Mar;123(3):958-65. doi: 10.1172/JCI64096. Epub 2013 Mar 1. PMID: 23454758; PMCID: PMC3582124
[3] Semba RD. Vitamin A, immunity, and infection. Clin Infect Dis. 1994 Sep;19(3):489-99. doi: 10.1093/clinids/19.3.489. PMID: 7811869
[4] Carr AC, Maggini S. Vitamin C and Immune Function. Nutrients. 2017 Nov 3;9(11):1211. doi: 10.3390/nu9111211. PMID: 29099763; PMCID: PMC5707683
[5] Albert Sanchez, J. L. Reeser, H. S. Lau, P. Y. Yahiku, R. E. Willard, P. J. McMillan, S. Y. Cho, A. R. Magie, U. D. Register, Role of sugars in human neutrophilic phagocytosis, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 26, Issue 11, November 1973, Pages 1180–1184, https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/26.11.1180
[6] Opposing Effects of Fasting Metabolism on Tissue Tolerance in Bacterial and Viral Inflammation https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(16)30972-2
[7] Sarkar D, Jung MK, Wang HJ. Alcohol and the Immune System. Alcohol Res. 2015;37(2):153–5. PMCID: PMC4590612
[8] Acrylamide in food https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/food-nutrition/food-safety/chemical-contaminants/food-processing-induced-chemicals/acrylamide.html
[9] Fast food fever: reviewing the impacts of the Western diet on immunity https://nutritionj.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/1475-2891-13-61.pdf
[10] Cancer: Carcinogenicity of the consumption of red meat and processed meat https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/cancer-carcinogenicity-of-the-consumption-of-red-meat-and-processed-meat
[11] Samraj AN, Pearce OM, Läubli H, Crittenden AN, Bergfeld AK, Banda K, Gregg CJ, Bingman AE, Secrest P, Diaz SL, Varki NM, Varki A. A red meat-derived glycan promotes inflammation and cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 13;112(2):542-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417508112. Epub 2014 Dec 29. PMID: 25548184; PMCID: PMC4299224
[12] Jianqin S, Leiming X, Lu X, Yelland GW, Ni J, Clarke AJ. Effects of milk containing only A2 beta casein versus milk containing both A1 and A2 beta casein proteins on gastrointestinal physiology, symptoms of discomfort, and cognitive behavior of people with self-reported intolerance to traditional cows' milk. Nutr J. 2016 Apr 2;15:35. doi: 10.1186/s12937-016-0147-z. Erratum in: Nutr J. 2016;15(1):45. PMID: 27039383; PMCID: PMC4818854
[13] Meditation or Exercise for Preventing Acute Respiratory Infection: A Randomized Controlled Trial https://www.annfammed.org/content/10/4/337.long
[14] Optimism is associated with exceptional longevity in 2 epidemiologic cohorts of men and women https://www.pnas.org/content/116/37/18357
[15] Segerstrom SC. Optimism and immunity: do positive thoughts always lead to positive effects? Brain Behav Immun. 2005 May;19(3):195-200. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2004.08.003. PMID: 15797306; PMCID: PMC1948078
[16] Acrylamide and Cancer Risk https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/diet/acrylamide-fact-sheet
[17] Phruitful Dish by Dr. Dylan Cutler http://phruitfuldish.com/2020/02/12/7-evidence-based-ways-to-get-a-better-sleep-tonight/
[18] Rondanelli M, Opizzi A, Monteferrario F, Antoniello N, Manni R, Klersy C. The effect of melatonin, magnesium, and zinc on primary insomnia in long-term care facility residents in Italy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011 Jan;59(1):82-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.03232.x. PMID: 21226679
[19] Costello RB, Lentino CV, Boyd CC, O'Connell ML, Crawford CC, Sprengel ML, Deuster PA. The effectiveness of melatonin for promoting healthy sleep: a rapid evidence assessment of the literature. Nutr J. 2014 Nov 7;13:106. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-13-106. PMID: 25380732; PMCID: PMC4273450







 This article changed my life!
This article changed my life!
 This article was informative.
This article was informative.
 I have a medical question.
I have a medical question.
 Ask a Question
Ask a Question

 This article contains incorrect information.
This article contains incorrect information.
 This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.
This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.